| Home » Technology & Science » Space News |
Star death creates Red Square nebula
Extreme symmetry suggests the star’s surroundings are extremely still
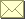
 | This
picture, of the Red Square nebula surrounding the hot star MWC
922, was taken with infrared adaptive optics imaging at Palomar
and Keck Observatories. |
Space.com |
Most Popular |
| |||||
If symmetry is a sign of splendor, then the newly discovered Red Square nebula is one of the most beautiful objects in the universe.
Seen in the infrared, the nebula resembles a giant, glowing red box in the sky, with a bright white inner core. A dying star called MWC 922 is located at the system’s center and spewing its innards from opposite poles into space. (A nebula is an interstellar cloud of gas, dust and plasma where stars can both emerge and die.)
“This spectacular event is the death of a star,” said study team member James Lloyd of Cornell University.
After MWC 922 ejects most of its material into space, it will contract into a dense stellar corpse known as a white dwarf, shrouded by clouds of its own remains.
The Red Square nebula discovery is detailed in the April 13 issue of the journal Science.
Almost perfect
What
is particularly astonishing about the Red Square, the researchers say,
is the degree of symmetry seen in lines, or “rungs,” that bisect its
surface. The rungs appear as shadows, and their makeup is uncertain.
“The high degree of regularity in this case may point to the intriguing possibility that these bands are shadows cast by periodic ripples or waves on the surface of an inner disk close to the star at the heart of the system," Lloyd said.
The Red Square ranks among the most symmetrical objects ever observed by scientists. “If you fold things across the principle diagonal axis, you get an almost perfect reflection symmetry,” said study leader Peter Tuthill from the University of Sydney in Australia. “This makes the Red Square nebula the most symmetrical object of comparable complexity ever imaged.”
The Red Square’s extreme symmetry suggests the star’s surroundings are extremely still and not buffeted by external stellar winds or other turbulence.
The researchers propose that similar conditions are contributing to the extreme symmetry of another system, the Red Rectangle, whose central star is cooler than that of the Red Square.
“The Red Rectangle is mostly symmetrical, but it has some asymmetries,” Lloyd told SPACE.com. “It wasn’t clear whether it was because the outflow was very symmetrical or whether material in the outflow was encountering some other material” which introduced the symmetry.
|
Adaptive optics
Tuthill
and Lloyd spotted the Red Square using the 200-inch Hale Telescope at
Caltech’s Palomar Observatory and the Keck-2 Telescope in Hawaii.
Click for related content |
Both telescopes utilize a relatively new type of imaging called adaptive optics, which uses a laser guide star as a reference and a rapidly deforming mirror to correct image distortions from the Earth’s atmosphere in real time.
Adaptive optics “acts like a myopia cure for a telescope,” Lloyd said.
MORE FROM SPACE NEWS |
| Add Space News headlines to your news reader: |
| ||||