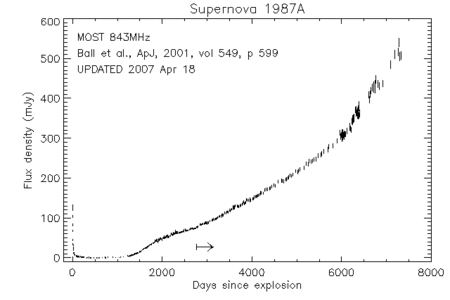
Supernova 1987A: MOST light curve at 843 MHz
SN1987A in the Large Magellanic Cloud is the
nearest supernova explosion observed in over 300 years. Radio
emission from SN1987A was first detected with the MOST on 1987
February 25.23 UT (Turtle et al. 1987, Nature, 327, 38), two days
after the detection of neutrinos. MOST continued to monitor the
evolution of the radio emission through its decline, quiescence,
recovery on 1990 July 5, and subsequent monotonic rise up to the
present. The most recent data show a clear steepening in the rate of
increase of flux density. The closer monitoring around day 6000 was
triggered by an apparent increase in short-term variability.
843 MHz flux densities up to and including 1994 September 3
were reported by Ball et al. 1995 (ApJ, 453, 864). Data from 1994
September 17 to 2000 May 5 are given in Ball
et al. 2001 (ApJ, 549, 599). The complete light curve is shown below.
- Download the full MOST datafile from 1987 to the present (22 kB)
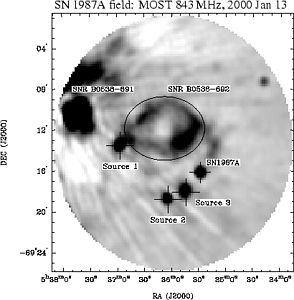
- Download the MOST radio image of the SN1987A field (92 kB, gzipped ps)
- Download the MOST light curve at 843 MHz (11 kB, gzipped ps)
| 
|
If you use any MOST images or data for SN1987A in
your publication, please cite
Ball, L., Crawford, D.F., Hunstead, R.W., Klamer,
I., & McIntyre, V.J., ``Radio supernova 1987A at 843 MHz'' (2001, ApJ,
549, 599-607)
and this website, and include the acknowledgement:
"The MOST is operated by the University of Sydney and supported in part
by grants from the Australian Research Council."
[an error occurred while processing this directive]